The <menu> tag defines a list of commands. It is used for creating context menus, toolbars, listing form controls, and commands.
A context menu consists of a <menu> element that has <menuitem> elements for each selectable option, as well as <hr> elements that break up the content of the menu into sections with the help of separator lines.
A toolbar menu consists of a <menu> element. Here, the content of this element can be described in two ways:
- It can contain an unordered list of items that are represented by the HTML <li> element.
- It can contain flow content that describes the accessible options and commands.
Each list item in <menu> tag starts with the <li> or the <menuitem> elements.
Syntax
The <menu> tag comes in pairs. The content is written between the opening (<menu>) and closing (</menu>) tags.
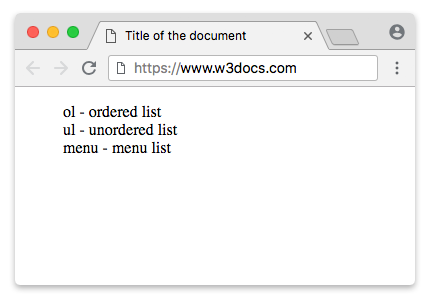
Example of the HTML <menu> tag used with <ol> and <ul> tags:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
menuitem {
display: block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<menu>
<menuitem>ol - ordered list</menuitem>
<menuitem>ul - unordered list</menuitem>
<menuitem>menu - menu list</menuitem>
</menu>
</body>
</html>Result
Example of the HTML <menu> tag for creating a context menu:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div style="background:#1c87c9; padding: 20px; text-align:center; color:#ffffff;" contextmenu="menuexample">
<p>Right-click inside this box to open the context menu</p>
<menu type="context" id="menuexample">
<menuitem label="Refresh" onclick="window.location.reload();"></menuitem>
<menu label="Share on...">
<menuitem label="Twitter" onclick="window.open('//twitter.com/intent/tweet?text=' + window.location.href);"></menuitem>
<menuitem label="Facebook" onclick="window.open('//facebook.com/sharer/sharer.php?u=' + window.location.href);"></menuitem>
</menu>
<menuitem label="Email This Page" onclick="window.location='mailto:?body='+window.location.href;"></menuitem>
</menu>
</div>
<p><span style="color:red;">Reminder:</span> This works only in Firefox.</p>
</body>
</html>The difference between the <menu> and <ul> tags
These two elements have similar behavior. Both the <menu> and <ul> elements are used to create an unordered lists. The main difference between them is that the <menu> tag contains display items, while the <ul> tag contains interactive ones.
Attributes
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| label | text | Defines a visible label for the menu. |
| type | popup toolbar context |
Defines the type of the menu. |
The <menu> tag also supports the Global attributes and the Event Attributes.
How to style <menu> tag?
Common properties to alter the visual weight/emphasis/size of text in <menu> tag:
- CSS font-style property sets the style of the font. normal | italic | oblique | initial | inherit.
- CSS font-family property specifies a prioritized list of one or more font family names and/or generic family names for the selected element.
- CSS font-size property sets the size of the font.
- CSS font-weight property defines whether the font should be bold or thick.
- CSS text-transform property controls text case and capitalization.
- CSS text-decoration property specifies the decoration added to text, and is a shorthand property for text-decoration-line, text-decoration-color, text-decoration-style.
Coloring text in <menu> tag:
- CSS color property describes the color of the text content and text decorations.
- CSS background-color property sets the background color of an element.
Text layout styles for <menu> tag:
- CSS text-indent property specifies the indentation of the first line in a text block.
- CSS text-overflow property specifies how overflowed content that is not displayed should be signalled to the user.
- CSS white-space property specifies how white-space inside an element is handled.
- CSS word-break property specifies where the lines should be broken.
Other properties worth looking at for <menu> tag:
- CSS text-shadow property adds shadow to text.
- CSS text-align-last property sets the alignment of the last line of the text.
- CSS line-height property specifies the height of a line.
- CSS letter-spacing property defines the spaces between letters/characters in a text.
- CSS word-spacing property sets the spacing between words.
Browser support
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| ✕ | 8+ | ✕ | ✕ |
Practice Your Knowledge
Quiz Time: Test Your Skills!
Ready to challenge what you've learned? Dive into our interactive quizzes for a deeper understanding and a fun way to reinforce your knowledge.